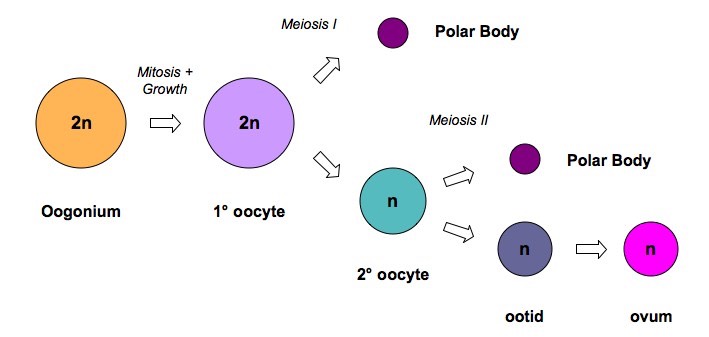
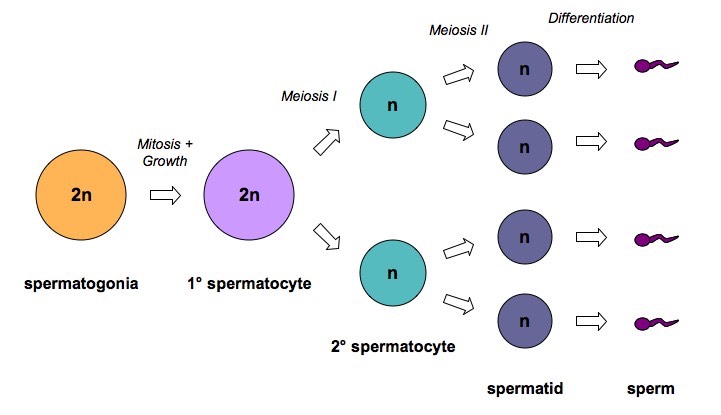
1.
Define the terms stimulus, response, and reflex
in the context of behavior
·
Stimulus: A change in the environment (external or internal)
that is detected by a receptor
·
Response: A change in an organism (an action) resulting from a
stimulus
·
Reflex: A type of response that is rapid and involuntary
(unconscious)
2.
Explain the role of receptors, sensory neurons,
relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals
to stimuli
·
Receptors transform stimuli into electrical nerve impulses
·
Sensory neurons relay the nerve impulse to the central nervous
system (via the dorsal root of the spinal cord)
·
Relay neurons (also called interneurons or
connector neurons) transmit nerve impulses within the CNS
·
Motor neurons receive nerve impulses from the CNS (via the
ventral root) and relays the signal to an effector
·
Effectors (muscles or glands) produce a response to the stimulus
·
Synapses are the junctions between two nerve cells and
transmission of a signal across these junctions require chemical neurotransmitters
3.
Draw
and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the
spinal cord and its spinal nerves, relay neuron, motor neuron and effector
4. Explain how animal responses can be affected by
natural selection, using two examples
Natural selection describes the process
by which the frequency of an inheritable characteristic changes as a result of
external (environmental) agents
These beneficial inheritable traits
(adaptations) can include instinctive behaviours such as migrating, foraging,
hunting, communication, etc.
Example: Blackcap Migration
Patterns
§ The
blackcap (Sylvia atricapilla) exhibits behavioural variation in its
migration patterns from its summer breeding grounds in Germany
§ Historically,
most blackcaps migrated south to Spain (warmer climate in winter) with a
minority migrating west to the UK (closer, but cooler)
§ With
a rise in global temperatures, more blackcaps are now migrating west to the UK
(more favourable survival prospects increase allele frequency)
Example: House Sparrow Feeding
Behaviours
§ The
house sparrow (Passer domesticus) will chirp and gape as a
fledgling in order to be fed by its parents
§ In
a nest of chicks, those which chirp louder and gape more obviously are more
likely to be fed more and survive longer
§ Hence
the alleles responsible for chirping and gaping are passed to offspring
increasing prevalence of the behaviour