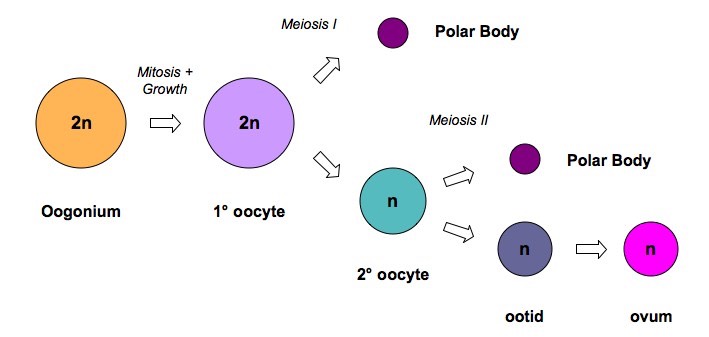
- Oogenesis describes the production of female gametes (ova) within the ovary
- The process begins during foetal development, when a large number of cells (oogonia) are formed by mitosis before undergoing a period of growth
- These cells begin meiosis but are arrested in prophase I until puberty
- At puberty, some follicles continue to develop each month is response to FSH secretion
- These follicles complete the first meiotic division to form two cells of unequal size
- The cell with less cytoplasm is a polar body (which degenerates), while the larger cell forms a secondary oocyte
- The secondary oocyte begins the second meiotic division but is arrested in prophase II (until fertilisation)
- It is released from the ovary (ruptured follicle develops into corpus luteum) and, if fertilisation occurs, will complete meiosis
- The second meiotic division will produce an ovum and a second polar body
Overview of Oogenesis
2. What are the steps in spermatogenesis
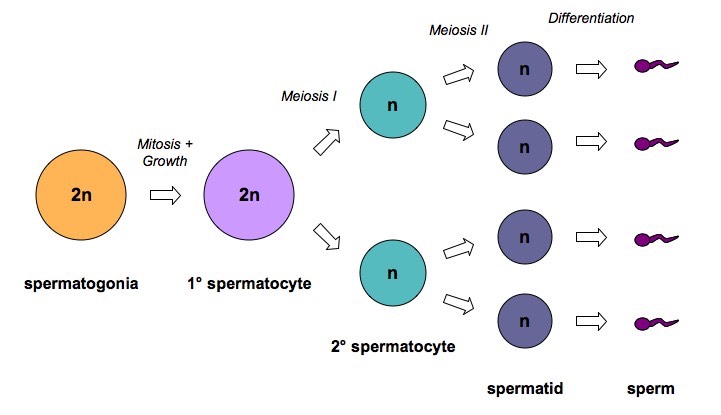
- Spermatogenesis describes the production of spermatozoa (sperm) in the seminiferous tubules of the testes
- The first stage of sperm production requires the division of germline epithelium by mitosis
- These cells (spermatogonia) then undergo a period of growth
- This is followed by two meiotic divisions that result in four haploid daughter cells
- These haploid cells then differentiate to form sperm cells
- The developing sperm cells are nourished throughout by the Sertoli cells
Overview of Spermatogenesis
3. What are the similarities and differences between the two?
Similarities:
- Both processes result in the formation of haploid gametes
- Both processes involve mitosis, growth and meiosis
Differences:

No comments:
Post a Comment